Frequent dizziness, tinnitus, flies in front of the eyes, a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head are caused not only by fatigue.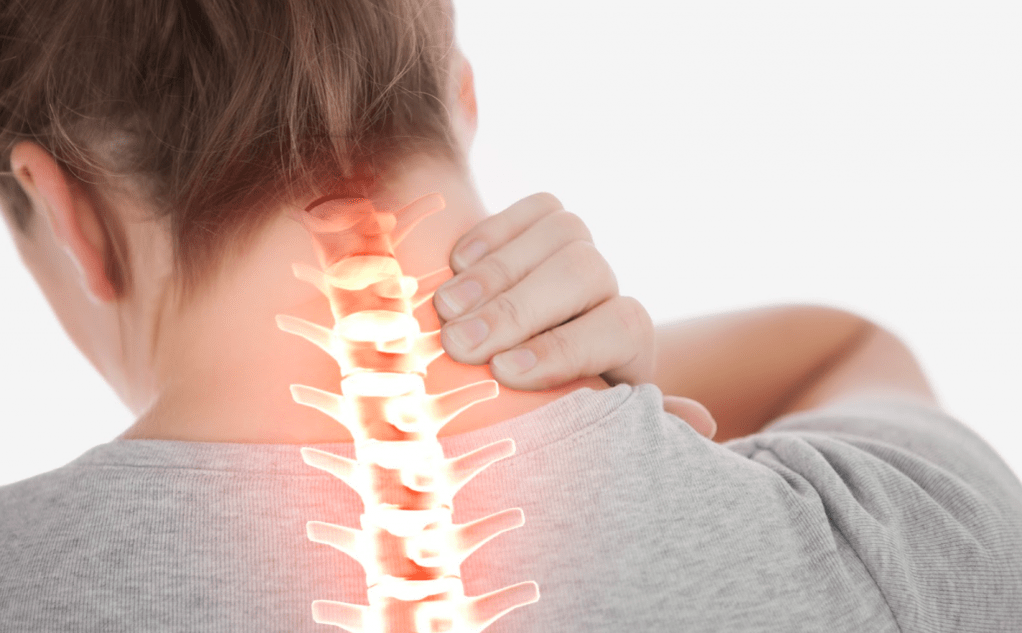 They are often caused by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. Headaches with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are a typical manifestation of the disease. It is impossible to get rid of them for a long time without affecting the cause.
They are often caused by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. Headaches with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are a typical manifestation of the disease. It is impossible to get rid of them for a long time without affecting the cause.
The mechanism of disease development
Degeneration of the intervertebral cartilage and bone tissue in the cervical spine causes clinical symptoms already in the early stages. The proliferation and displacement of vertebral fragments inevitably leads to disruption of blood flow, hydration and inadequate nutrition of brain structures. The causes of spinal deformity in the neck area are:
- congenital disorders of bone structure.
- bodily injury
- inappropriate attitude
- weakness?
- portliness;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar or thoracic regions.
In almost half of the cases, the pathology is found in middle-aged and young people, more often in women. Its development is facilitated by the prolonged incorrect position of the head during sleep, sitting at the desk, during telephone conversations and traveling in transport. The progression of osteochondrosis is accelerated by the habit of sleeping on high pillows. The mobility of this part of the body, the smaller size of the vertebrae compared to other parts, the location of a large number of large vessels and nerve trunks, determine the early onset of symptoms. Pain syndrome is the main.
Fragments of collapsing discs and damaged vertebrae compress the vertebral artery and the nerve plexuses around it. Prolonged compression causes narrowing of the vascular lumen, slowing of blood flow, and reduced oxygen supply to the tissues. Malnutrition, hypoxia and subsequent cerebral ischemia are exacerbated by compression of the nerve trunks by osteophytes - rhizopathy.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
In most cases, headaches and other symptoms of pathology are secondary or vertebrate in nature - they are caused by pathological processes not in the brain, but in the adjacent spine.
- Reflex headache - dull pain. Occurs when the first three vertebrae are affected. It starts from the upper part of the neck, extends to the occipital and parietal part and then covers the temples and the forehead. Most of the time it is unilateral, it looks like a classic migraine. It lasts from half an hour to several days, increases with tilting or rotation of the head, active physical energies.
- If osteochondrosis affects the fourth and fifth vertebrae, cervical brachialgia develops. The danger lies in the resemblance to a heart attack. The pain is unilateral, sharp, burning, covers the neck, shoulder and radiates down the scapula, into the hypochondrium, sometimes into the forearm and arm.
- Myocardial infarction causes the so-called cervical migraine. The pulse or pressure pain from the side of the neck spreads along one side, covering part of the occipital, crown, temple and reaches the overlying arches.
In severe cases, additional symptoms are observed: photophobia, redness of the eyes, nausea, physical weakness.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can cause several types of vascular dystonia:- with frequent headaches
- Violations of thermoregulation, intracranial pressure, respiration
- spasmodic mood swings.
With significant pinching of the spinal nerves, speech disorders, numbness of the tongue, loss of sensitivity of the fingers. A person becomes like a drunk or under the influence of psychotropic drugs: he speaks vaguely, does not immediately respond to a call to himself. In advanced cases, inadequate tissue nutrition and reduced blood supply lead to a steady increase in intracranial pressure, decreased vision and hearing.
Diagnostics
With complaints of poor health in case of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, it is necessary to contact a neurologist. During the examination, the doctor determines the origin of the pain. For this purpose, it uses the following methods:
- presses with the fingers in the area of the cervical vertebrae at those points where the nerve roots protrude: the emerging pain reaction indicates headache.
- presses points near the bony protrusions below the lower extremities of the ears: a painful attack after this clearly signals the development of a cervical migraine as a result of mechanical compression.
To accurately diagnose cervical osteochondrosis, some organic studies are prescribed. X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography remain the top. With their help, the pathological changes that have occurred in the structure of bones, cartilage and soft tissues are visualized.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The drugs are designed to eliminate the symptoms, restore normal blood circulation and industrial the entire cervical spine.
- NSAIDs, analgesics, muscle relaxants and anticonvulsants are used to relieve pain.
- Reducing herbal manifestations, improving venous outflow and preventing swelling in the affected area help with vasodilators - vasodilators.
- Products that contain B vitamins and magnesium help to improve the nutrition of nervous tissues and reduce side effects.
- At the same time, patients are recommended drugs to regulate blood pressure, correct heart rate.
- Many patients experience sedatives, antidepressants, sedatives.
Depending on the severity of the condition, the course of treatment is short or long. Painkillers are used for one or several days. Means that normalize blood flow and vitamins - in cycles of 2-3 months. To maintain the effect of the drugs, physiotherapy is prescribed:
- electrophoresis?
- valnotherapy
- darsonvalization;
- massage collar
- needle and reflexology.
In case of exacerbations, the use of therapeutic bandages that support the neck muscles is indicated.
In the absence of worsening osteochondrosis, therapeutic exercises help to stop and prevent the symptoms of VSD. Exercise helps strengthen the neck muscles, relieves spasms, improves the elasticity of blood vessels and the connecting device of the vertebral joints. The exercises include movements for stretching soft tissues: deep head tilts, turns, rotations.
Patients with osteochondrosis complicated by VSD should carefully organize their sleeping area. You should only rest on an orthopedic mattress and pillow, do not drink too much liquid at night to avoid swelling. It is necessary to avoid work and hobbies related to the unfavorable position of the cervical vertebrae: throwing backwards or low tilt of the head.